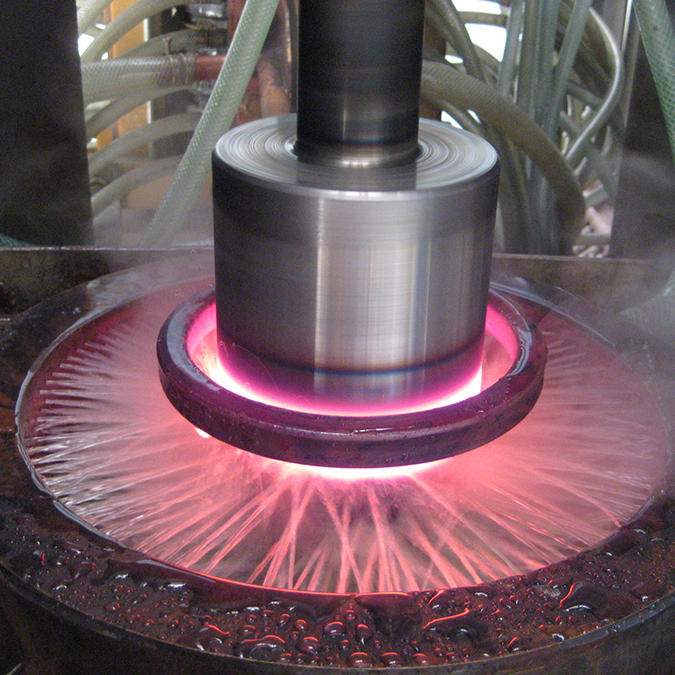
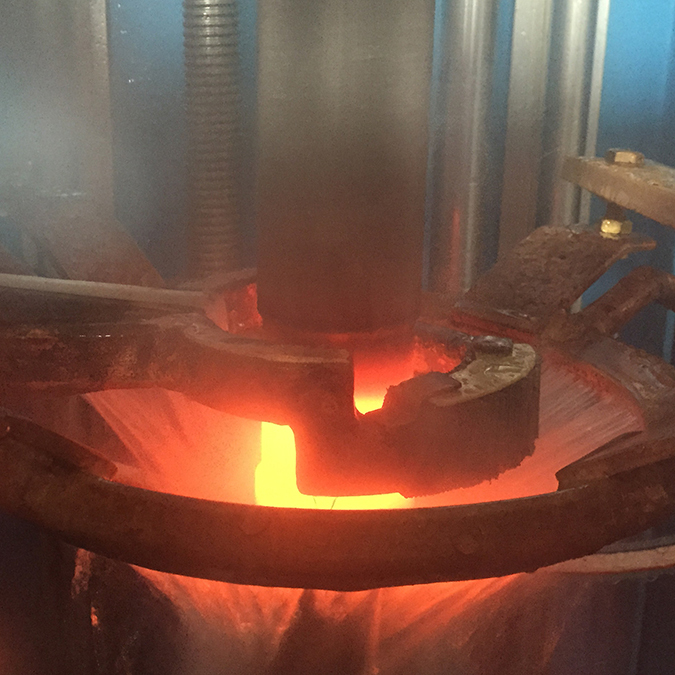
induction hardening machine
Products Description
Induction hardening is a form of heat treatment in which a metal part is heated by electromagnetic induction and then quenched, increase the hardness and brittleness of metal part.
Induction hardening equipment is widely used for the surface or inner hardening of steel.
Induction hardening process can be done in two different ways: static and scan hardening
Advantages of Induction hardening
• No physical contact hardening
• Scan/ Stationary hardening
• Short time (a few seconds) hardening increase production and improve quality
• CNC or PLC Control heating and cooling during hardening
Duolin Induction hardening equipments provide induction hardening solution for shaft, gear, roller, steel plate etc. The frequency of induction heating machines is from 1 KHz to 400KHz, which work with CNC or PLC quenching machines.

| Power | 4-1500KW |
| Frequency | 0.5-400KHz |
| Hardening Depth | 0.5-10mm |
| Mechanical Fixture | CNC or PLC Control |
| Application | Gear, shaft, pipe, bearing, pump fitting, steel plate, roller,wheel,bars |
|
Case depth [mm] |
Bar diameter [mm] |
Frequency [kHz] |
Model |
| 0.8 to 1.5 |
5 to 25 |
200 to 400 |
HGP30 |
| 1.5 to 3.0 |
10 to 50 |
10 to 100 |
Ultrasonic frequency series (10-30KH) |
|
>50 |
3 to 10 |
Medium Frequency series (1-8KHz) |
|
| 3.0 to 10.0 |
20 to 50 |
3 to 10 |
Ultrasonic/ Medium frequency series (10-30KH) |
|
50 to 100 |
1 to 3 |
Medium Frequency series (1-8KHz) |
|
|
>100 |
1 |
1 Medium Frequency series (1-8KHz) |
The main benefit of induction heating for hardening is that it takes just a few seconds.
Hardening test laboratory to check the hardening depth and hardness
• Precise and fast heating for work pieces
• Reliability, consistency
• Constant power or constant voltage control mode
• Continuously working, 24 hours non-stop
• Less interference to others equipment in workshop (Proved by CE)
• IGBT inversion technology &LC series circuit design achieve energy saving up to 15%-30% compared with SCR technology
• Easy to operate and maintain
• Installation can be one very easily according our manual

What we need to know before offer induction hardening system?
1: The drawing of hardening parts
2: Material and hardening position
3: The hardness and hardening depth required
4: Require hardening production or not